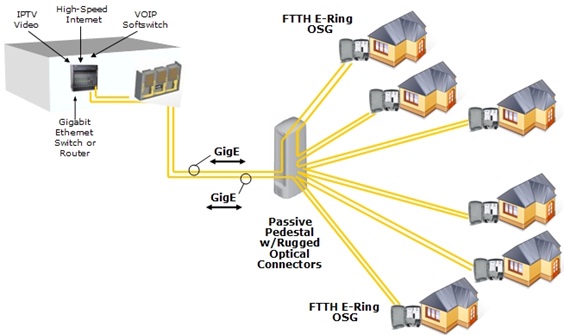
PON is the abbreviation of passive optical network, which only uses fiber and passive components like splitters and combiners. EPON (Ethernet PON) and GPON (Gigabit PON) are the most important versions of passive optical networks, widely used for Internet access, voice over Internet protocol (VoIP), and digital TV delivery in metropolitan areas. Today we are going to talk about the differences between them.
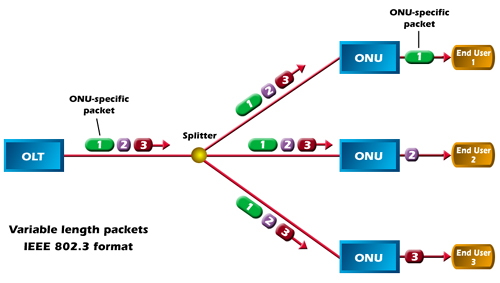
Technology Comparison
EPON is based on the Ethernet standard 802.3 that can support the speed of 1.25 Gbit/s in both the downstream and upstream directions. It is well-known as the solution for the "first mile" optical access network. While GPON, based on Gigabit technology, is designated as ITU-T G.983 which can provide for 622 Mbit/s downstream and 155 Mbit/s upstream. GPON is an important approach to enable full service access network. Its requirements were set force by the Full Service Access Network (FASN) group, which was later adopted by ITU-T as the G.984.x standards–an addition to ITU-T recommendation, G.983, which details broadband PON (BPON).
As the parts of PON, they have something in common. For example, they both can be accepted as international standards, cover the same network topology methods and FTTx applications, and use WDM (wavelength-division multiplexing) with the same optical frequencies as each other with a third party wavelength; and provide triple-play, Internet Protocol TV (IPTV) and cable TV (CATV) video services.
Costs Comparison
No matter in a GPON or in an EPON, the optical line terminal (OLT), optical network unit (ONU) and optical distribution network (ODN) are the indispensable parts, which are the decisive factor of the costs of GPON and EPON deployments.
The cost of OLT and ONT is influenced by the ASIC (application specific integrated circuit) and optic module. Recently, the chipsets of GPON are mostly based on FPGA (field-programmable gate array), which is more expensive than the EPON MAC layer ASIC. On the other hand, the optic module’s price of GPON is also higher than EPON’s. When GPON reaches deployment stage, the estimated cost of a GPON OLT is 1.5 to 2 times higher than an EPON OLT, and the estimated cost of a GPON ONT will be 1.2 to 1.5 times higher than an EPON ONT.
We all know that the ODN is made up of fiber cable, cabinet, optical splitter, connector, and etc. In the case of transmitting signals to the same number of users, the cost of EPON and GPON would be the same.
Summary
Nowadays, since many experts have different opinions on GPON and EPON. Thus, there is no absolute answer to determine which is better. But one thing is clear: PON, which possesses the low cost of passive components, has made great strides driven by the growing demand for faster Internet service and more video. Also, fiber deployments will continue expanding at the expense of copper, as consumer demands for "triple-play" (video, voice and data) grow.
Originally published at http://www.chinacablesbuy.com/comparison-between-epon-and-gpon.html