As the bandwidth demands grow rapidly, data centers have to achieve ultra-high density in cabling to accommodate all connections. MPO/MTP technology with multi-fiber connectors offers ideal conditions for high-performance data networks in data centers. This article will introduce information about MPO/MTP solutions, such as MPO/MTP trunk cable, MPO/MTP harness cable and MPO/MTP cassettes.
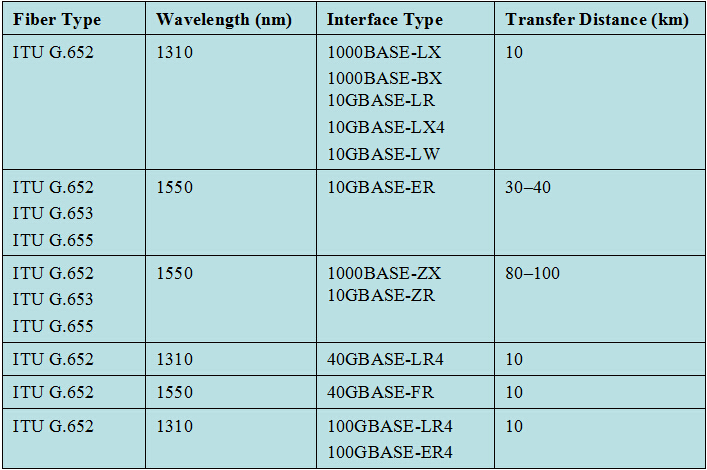
MTP/MPO Trunk Cable
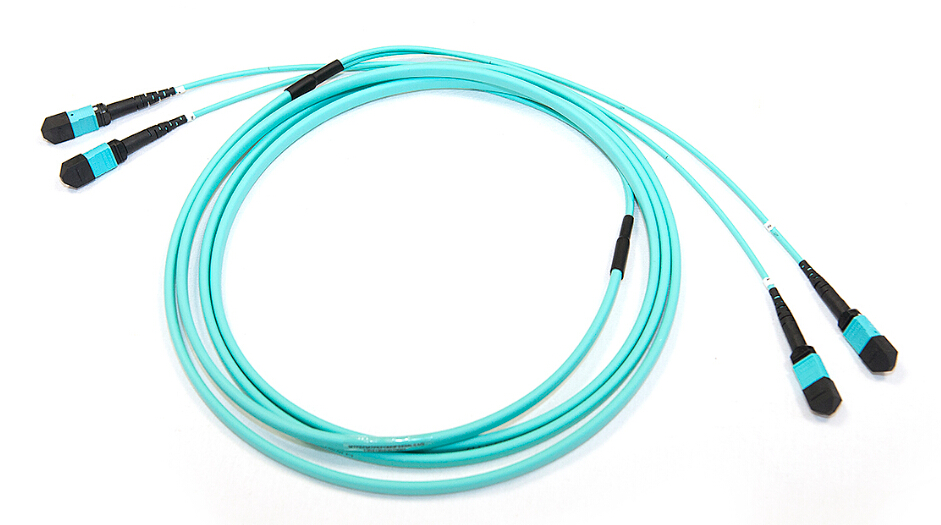
MTP/MPO trunk cables are terminated with the MTP/MPO connectors (as shown in the following figure). Trunk cables are available with 12, 24, 48 and 72 fibers. MTP/MPO trunk cables are designed for data center applications. The plug and play solutions uses micro core cable to maximize bend radius and minimize cable weight and size. Besides, MTP/MPO trunk cables also have the following advantages:
- Saving installation time–With the special plug and play design, MTP/MPO trunk cables can be incorporated and immediately plugged in. It greatly helps reduce the installation time.
- Decreasing cable volume–MTP/MPO trunk cables have very small diameters, which decrease the cable volume and improve the air-conditioning conditions in data centers.
- High quality–MTP/MPO trunk cables are factory pre-terminated, tested and packed along with the test reports. These reports serve as long-term documentation and quality control.

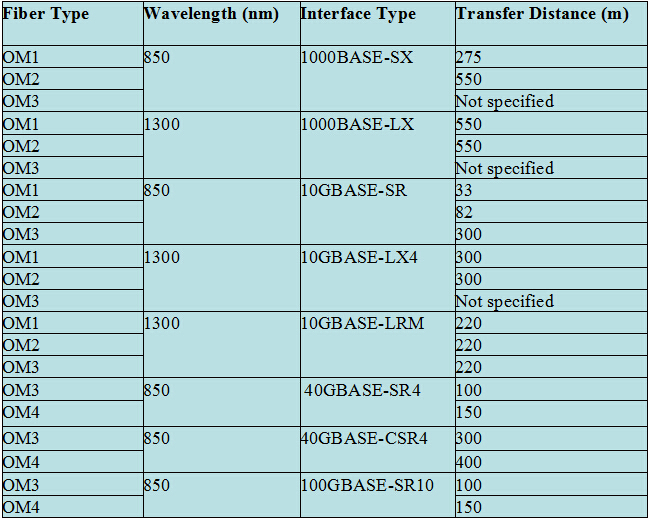
MPO/MTP Harness Cable
MPO/MTP harness cable (as shown in the following figure) is also called MPO/MTP breakout cable or MPO/MTP fan-out cable. This cable has a single MTP connector on one end that breaks out into 6 or 12 connectors (LC, SC, ST, etc.). It’s available in 4, 6, 8, or 12 fiber ribbon configurations with lengths about 10, 20, 30 meters and other customized lengths. MPO/MTP harness cable is designed for high density applications with required high performance. It’s good to optimize network performance. Other benefits are shown as below:
- Saving space–The active equipment and backbone cable is good for saving space.
- Easy deployment–Factory terminated system saves installation and network reconfiguration time.
- Reliability–High standard components are used in the manufacturing process to guarantee the product quality.

MPO/MTP Cassette
MPO/MTP cassette modules provide secure transition between MPO/MTP and LC or SC discrete connectors. They are used to interconnect MPO/MTP backbones with LC or SC patching. MPO/MTP Cassettes are designed to reduce installation time and cost for an optical network infrastructure in the premises environment. The modular system allows for rapid deployment of high density data center infrastructure as well as improved troubleshooting and reconfiguration during moves, adds and changes. Except for that, it has other advantages reflected in these sides:
as well as improved troubleshooting and reconfiguration during moves, adds and changes. Except for that, it has other advantages reflected in these sides:
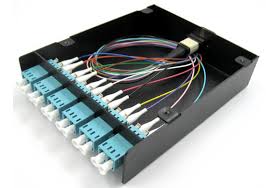 as well as improved troubleshooting and reconfiguration during moves, adds and changes. Except for that, it has other advantages reflected in these sides:
as well as improved troubleshooting and reconfiguration during moves, adds and changes. Except for that, it has other advantages reflected in these sides:- MPO/MTP interface–MPO/MTP components feature superior optical and mechanical properties.
- Optimized performance–Low insertion losses and power penalties in tight power budget, high-speed network environments.
- High density–12 or 24 fiber cassettes can be mounted in 1U scaling up to 72 or in 3U scaling up to 336 discrete LC connectors.
The above shows that the MPO/MTP system is a good solution for data center requirements. This high density, scalable system is designed to enable thousands of connections. Fiberstore offers a wide range of MPO/MTP trunk cables, harness cables and cassettes (or patch panels).
Originally published at http://www.china-cable-suppliers.com/mpomtp-solutions-for-high-density-applications.html